How to Move/Migrate a Full Git Repository From GitHub to GitLab Self-Hosted Instance

In this post, I’ll show you how to move a full git repository from GitHub to GitLab self-hosted instance. We’ve an old repository existing on github and we wanted to move it with all branches and commits to our gitlab stand alone server, so Here’s the steps we did:
Step 1: Create a new project on GitLab Self-Hosted Instance
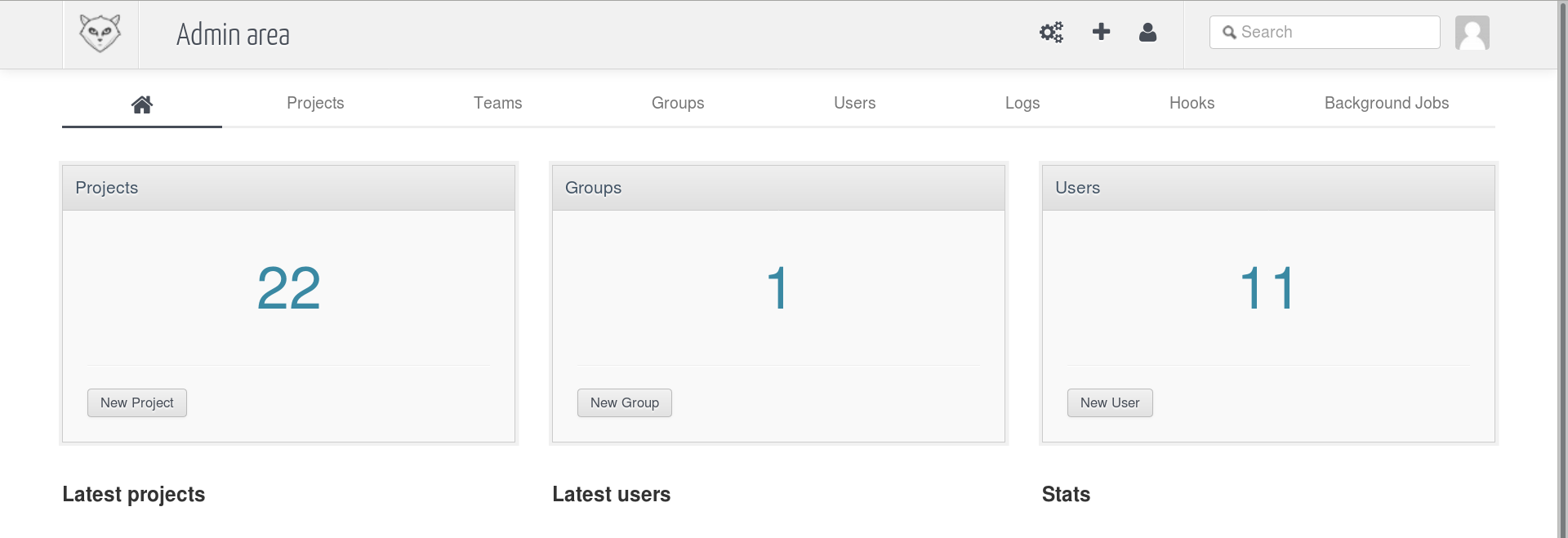
The first step is creating an empty repository on you GitLab Server, Login to your GitLab server and from the admin area select New Project As in the following image:
This will open a new window to enter the project details enter the name and select the Namespace as follow:
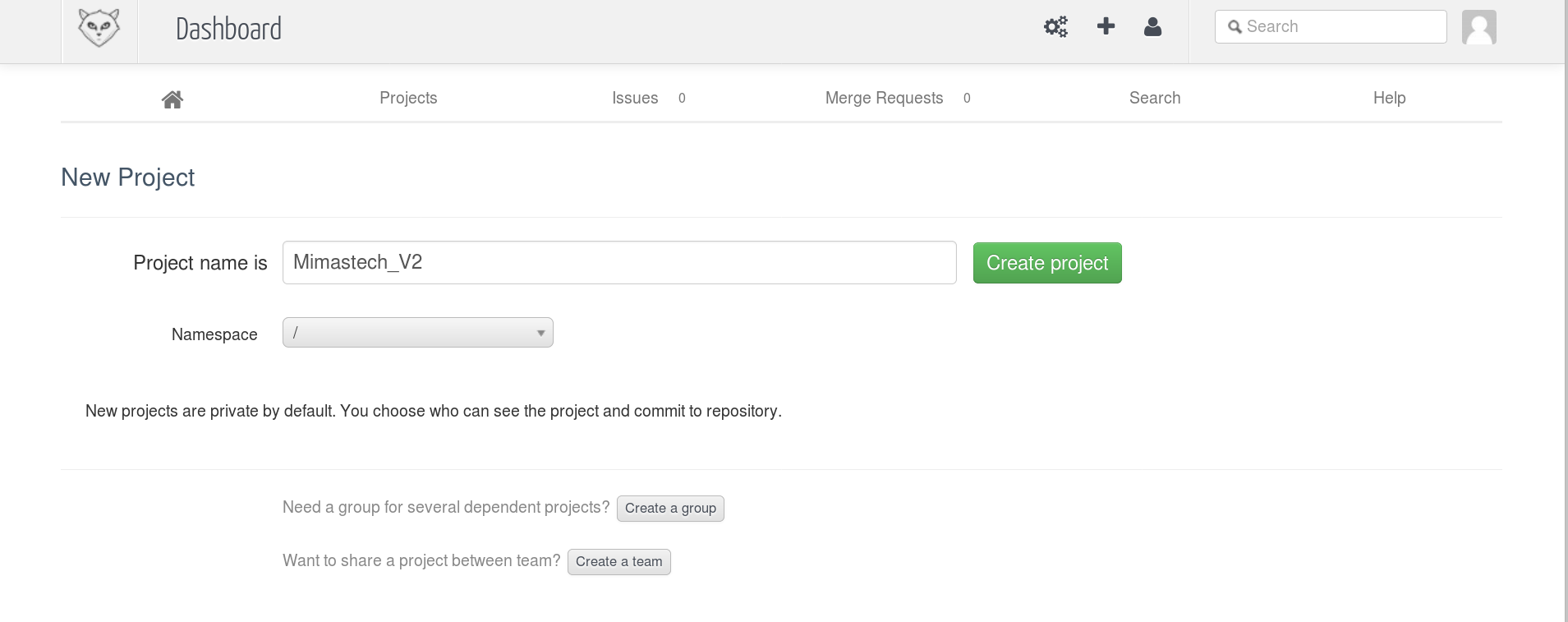 Once you click Create project, the new empty repo will be created. This all work on the GitLab Self-Hosted instance.
Once you click Create project, the new empty repo will be created. This all work on the GitLab Self-Hosted instance.
Step 2: Copy the entire GitHub repository to your machine
Now, we need to clone the entire GitHub repository to our local machine “your personal PC/Laptop”. Run the following command to simply copy the entire repository “master and all branches” to your local machine under temp folder with any name:
$ git clone --mirror git@github.com:mimastech/mimastech-ci.git Mimastech_V2
Cloning into bare repository 'Mimastech_V2'...
remote: Counting objects: 193850, done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (70/70), done.
remote: Total 193850 (delta 1746), reused 1690 (delta 1690), pack-reused 192090
Receiving objects: 100% (193850/193850), 111.33 MiB | 831.00 KiB/s, done.
Resolving deltas: 100% (129942/129942), done.
For the above output, we cloned the entire repository into a temp folder called Mimastech_V2 “The above command created this temp folder”
Step 3: Check What You Cloned From Github
Now, we do a simple check on our repository, run the following command:
$ cd Mimastech_V2 $ git branch 110 111 . . . hotfix * master
All branches are cloned.
Step 4: Remove Link to Old Repository
Now clear the link to the ORIGIN repository “GitHub” with the following command:
$ git remote rm origin Note: Some branches outside the refs/remotes/ hierarchy were not removed; to delete them, use: git branch -d 110 git branch -d 111 . . git branch -d hotfix git branch -d master
Step 5: Link Local Repository to the New Repository
Now link your local repository to your newly created GitLab repository using the following command:
$ git remote add origin <url to NEW repo>
<url to New repo> : found on the GitLab project you created in the first step.
Step 6: Push Local Repo to the New Repo on GitLab
Now push all your branches and tags with these commands:
$ git push origin --all Counting objects: 193819, done. Delta compression using up to 4 threads. Compressing objects: 100% (59947/59947), done. Writing objects: 100% (193819/193819), 111.32 MiB | 83.00 KiB/s, done. Total 193819 (delta 129923), reused 193812 (delta 129916) To git@gitlab.mimastech.com:mimastech_v2.git * [new branch] 110 -> 110 * [new branch] 111 -> 111 . . * [new branch] hotfix -> hotfix * [new branch] master -> master
Now, Your repo moved from github to gitlab self-hosted instance
If You Appreciate What We Do Here On Mimastech, You Should Consider:
- Stay Connected to: Facebook | Twitter | Google+
- Support us via PayPal Donation
- Subscribe to our email newsletters.
- Tell other sysadmins / friends about Us - Share and Like our posts and services
We are thankful for your never ending support.